It's about the visual perception of things, how humans put together a picture to make it a "unified whole".
The Gestalt theorum was discovered by a group of psychologists in Germany who studied perceptual organization.
Gestalt means literally means an "organized whole" , when parts identified individually have different characteristics to the whole. It's about how we look at things, how we are not concious of the parts but the whole object on its own. Parts are of secondary importance eventhough they may be clearly seen.
Here's an example
This is the vase/face profile. It's interesting how our eyes see things.
There are six principles of Gestalt theory:
Proximity

The principle of proximity states that things which are closer together will be seen as belonging together.
For example, the four squares on the left may be seen as one group while the four squares on the right may be seen as another group.
Similarity

The principle of similarity states that things which share visual characteristics such as shape, size, color, texture, value or orientation will be seen as belonging together.
For example, in the above example, there features three groups of white circles and three groups of black circles arranged in lines.
Continuation
The principle of continuity predicts the preference for continuous figures. We see the figure as two crossed lines instead of 4 lines meeting at the center.
For example, the dots that forms lines above may seem like 2 lines. However, they are four lines that meet in the center.
Closure

A tendency to close simple figures. This results in a effect of filling in missing information or organizing information which is present to make a whole
In the above example, one sees three pac mans or three circles with "v" cuts. However, if you look more carefully ones eyes can actually detect a triangle there formed by the three pac mans.
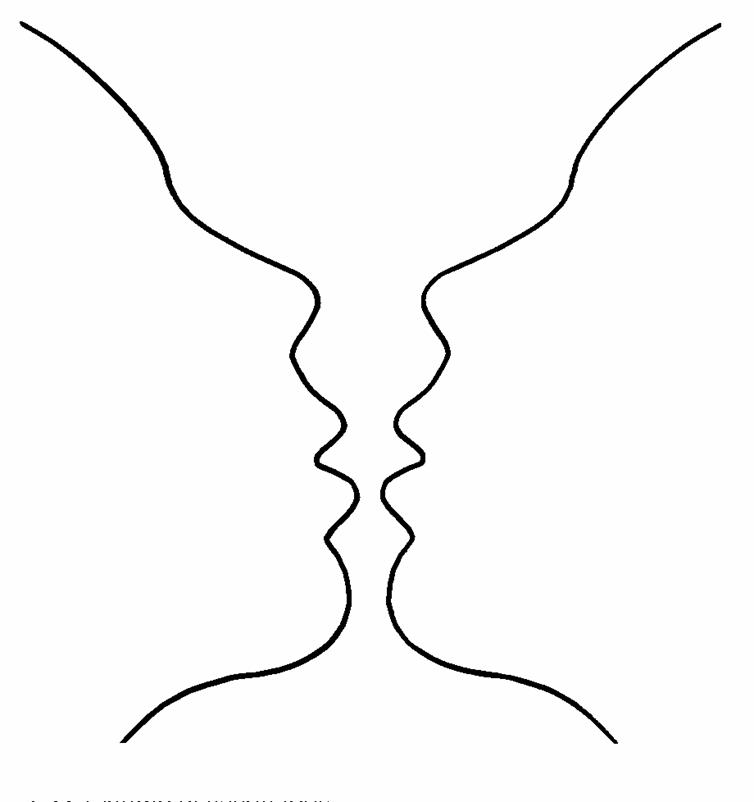
Symmetry

The principle of the symmetrical figure is that it is seen as a closed figure.
In the above example, one would be able to tell whether it's symmetrical or not by splitting the image in half.
Figure & Ground
It's a simple perception based on contrast to include abstract (non-visual) concepts e.g light and dark, positive and negative space etc.
In the example above, the human eye may first depict it as a young lady wearing a fur coat whereas it may also be depicted as an old lady with a hooked nose.
The End............>>>

No comments:
Post a Comment